In order for the translations in PARTdataManager (line description [Row Label], 2D derivation, PDF data sheet [Data sheet], etc.) are actually displayed, the following requirements must be met:
The desired catalog language must be set in PARTadmin (either as default of the program interface or explicitly).
The variables to be translated must be declared in PARTproject on the General tab page under Translatable variables [Translatable Variables].
Only then will they be displayed on the Translation tab page.
The translations must be displayed in black on the Translation tab page. A grayed-out display only indicates a translation suggest ion. To accept suggestions, click in the desired field and confirm with the Return key or click with the secondary mouse button in the desired field, select the context menu command Edit value and confirm with .
In the following the functions are exemplarily explained:
You can find some examples in the training catalog in the "translation " directory.[90]
Example 1 - Translation of a fixed term
[head_cap_bolts] German=Zylinderschrauben Default=Head Cap Screws English=Head Cap Screws
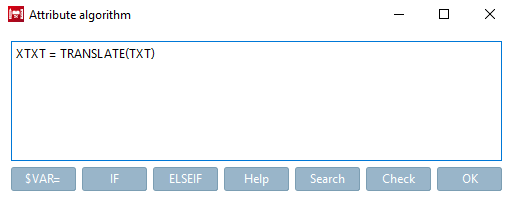
Insert the default term into the function TRANSLATE.
TRANSLATE('Head Cap Screws')For catalog language "german" the result would be: "Zylinderschrauben"
Example 2 - Translation of a variable
![[Note]](https://webapi.partcommunity.com/service/help/latest/pages/en/ecatalogsolutions/doc/images/note.png)
Note When using a variable in the form $VARIABLENNAME. its internal value is always returned.[a] However, if, for example, the visible, translated value is to be used in the line description [Row Label], data sheet [Data sheet], 2D derivation, etc., you can use the "TRANSLATE(VARIABLENNAME)" function.
[a] This is important because there are feature algorithms that access and work with the internal value.
Here in this example the function TRANSLATE is used together with a help variable.
[head_cap_bolts] German=Zylinderschrauben Default=Head Cap Screws English=Head Cap Screws
Here in the example, in the first step, a fixed value is assigned to a variable. Just as well you can directly reference to a table variable. On this see example 3.
A = 'Head Cap Screws'
Translation of the variable and assignment to a help variable.
B = TRANSLATE(A)
When querying "B" for catalog language "german" the result would be: "Zylinderschrauben"
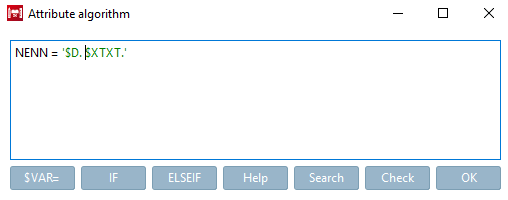
Example 3 - Translation of a variable: Translating text in the line description [Row Label]
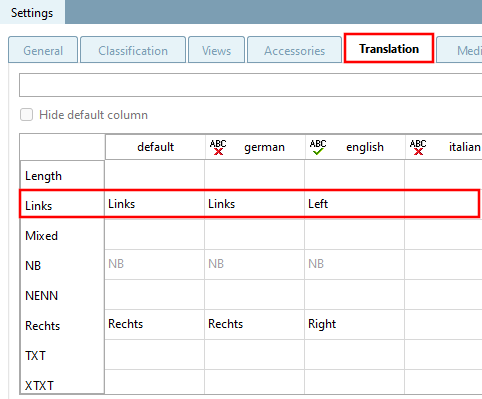
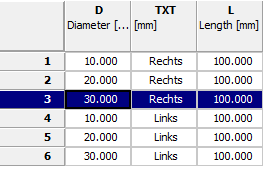
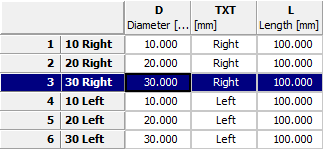
Initial situation: The TXT column contains values to be translated.
Example 4 - Translation of a variable: Translating text in the line description [Row Label]
![[Note]](https://webapi.partcommunity.com/service/help/latest/pages/en/ecatalogsolutions/doc/images/note.png)
Note When using a variable in the form $VARIABLENNAME. its internal value is always returned.[a] However, if, for example, the visible, translated value is to be used in the line description [Row Label], data sheet [Data sheet], 2D derivation, etc., you can also use the function "$VARIABLENNAME(SRC=VALDESC). " as an alternative to "TRANSLATE".
[a] This is important because there are feature algorithms that access and work with the internal value.
Initial situation: The TXT column contains values to be translated.
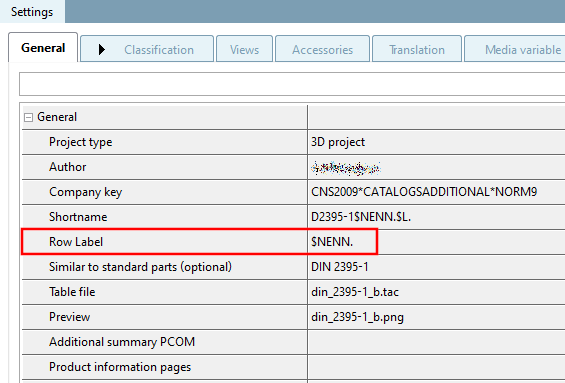
Enter the following expression under PARTproject -> tab page General -> Line description [Row Label], enter the following expression:
$TXT(SRC=VALDESC).
The following figures clarify the difference between the simple use of a variable an the above function:


![Line description [Row Label] with use of "$Variable name."](https://webapi.partcommunity.com/service/help/latest/pages/en/ecatalogsolutions/doc/resources/img/img_9da86ed61b4a406583d26a97bfd29bb5.png)
![Result: Row description [Row Label] NOT translated: The table value is translated by default](https://webapi.partcommunity.com/service/help/latest/pages/en/ecatalogsolutions/doc/resources/img/img_01004340c0254c87b259a7d7331e28ad.png)
![Line description [Row Label] using the function "$Variable name(SRC=VALDESC)."](https://webapi.partcommunity.com/service/help/latest/pages/en/ecatalogsolutions/doc/resources/img/img_11d95190696347b6a309329746e43cbd.png)
![Result: The line description [Row Label] is now also translated](https://webapi.partcommunity.com/service/help/latest/pages/en/ecatalogsolutions/doc/resources/img/img_59a33220934c4ecebbef4449792fc410.png)